Psychoanalysis: Meaning and Examples
The psychodynamic approach is rooted in the basic belief that people have unconscious desires, thoughts, feelings, and memories that, while outside of conscious awareness, still influence a person’s behavior.

The psychodynamic approach is rooted in the basic belief that people have unconscious desires, thoughts, feelings, and memories that, while outside of conscious awareness, still influence a person’s behavior.

How much do you know about personality psychology? Put your knowledge to the test with this brief quiz.

The anchoring bias is a type of heuristic that causes people to use the first they learn as a reference point for making future judgments and decisions. This anchoring effect is highly prevalent across a wide range of situations–and it’s also very difficult to overcome. In this article, learn more about what causes the anchoring…

Ever wonder how we form quick judgments about people? Implicit personality theory reveals how our unconscious beliefs shape the way we see others—and how those snap perceptions influence our daily interactions.
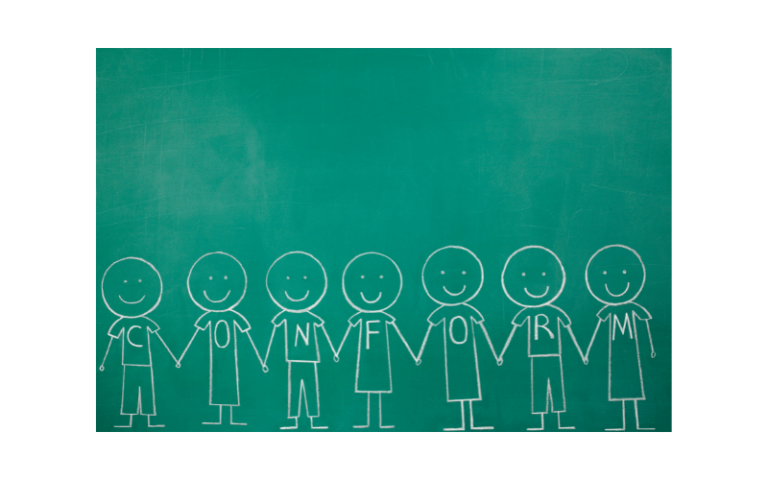

Conformity involves changing your behavior to align with other people’s behaviors, beliefs, and attitudes. People often conform to blend in with others in their social group. It is a type of social influence that compels people to behave in ways seen as “normal” for that specific group. Researchers define conformity as “aligning one’s attitude, opinion…

People are continuously inundated with endless amounts of information. External stimulation, internal thoughts, emotions, and other forces all compete for our attention. To deal with this, people utilize selective attention to tune out things they don’t need to focus on and concentrate on the important things. In this article, learn more about how selective attention…

Schedules of reinforcement determine when rewards are delivered and can affect the learning process.

Operant conditioning is a learning process that utilizes reinforcement and punishment to modify behavior. Learn more about how it works.

Classical conditioning is a learning process in which a neutral stimulus is paired with another stimulus that naturally produces a response. After repeated pairing, the previously neutral stimulus begins to evoke the response all on its own. Examples of classical conditioning include Pavlov’s experiment with dogs salivating at the sound of a bell and fear…

Albert Bandura was an influential Canadian-American psychologist known for his social learning theory, the Bobo doll experiment, observational learning, and self-efficacy. Throughout his long career, he left an indelible mark on the field of psychology and influenced other areas such as education and psychotherapy. In this article, learn more about Albert Bandura, including his early…

Social learning theory, also known today as social cognitive theory, is a theory proposed by psychologist Albert Bandura that explains how people learn through observation, imitation, and modeling. This model of learning suggests that both environmental and cognitive factors play a critical role in the acquisition of knowledge. In this article, learn more about the…
B. F. Skinner was born on March 20, 1904. He went on to become an influential psychologist who first described the learning process known as operant conditioning. Skinner played a pivotal role in behaviorism, a school of thought that suggested that all behavior was learned through conditioning processes. Skinner referred to himself as a radical…

Psychological experiments can tell us a lot about the human mind and behavior. Some of the best-known experiments have given us insights into topics such as conformity, obedience, attachment, and learning. There are many famous (and sometimes infamous) psychological experiments that have helped shape our understanding of the human mind and behavior. Such experiments offered…

Personality psychology explores the unique patterns of thoughts, feelings, and behaviors that define who we are. It seeks to uncover what drives our individual traits and how they influence our interactions with the world. Key Takeaways What Is Personality Psychology? Personality psychology is a branch of psychology that studies the patterns of thoughts, feelings, and…

Nonverbal communication is vital in how we share things with others and understand what others are trying to say. Communication is essential for successful interpersonal relationships, but it isn’t just the words you say that speak volumes. Your nonverbal signals—including body language and facial expressions—are forms of nonverbal communication that can carry much meaning. In…

People with a Type A personality are ambitious, competitive, and perfectionistic—which can be advantageous at times, and stressful in others.

Cognitive dissonance, the mental discomfort from holding conflicting beliefs, reveals how we rationalize choices and strive for inner consistency.
A cognitive bias is an unconscious systematic pattern of thinking that can result in errors in judgment. These biases stem from the brain’s limited resources and need to simplify the world to make faster decisions. Such biases are often the result of limitations or problems in memory, attention, and information processing. While such biases often…
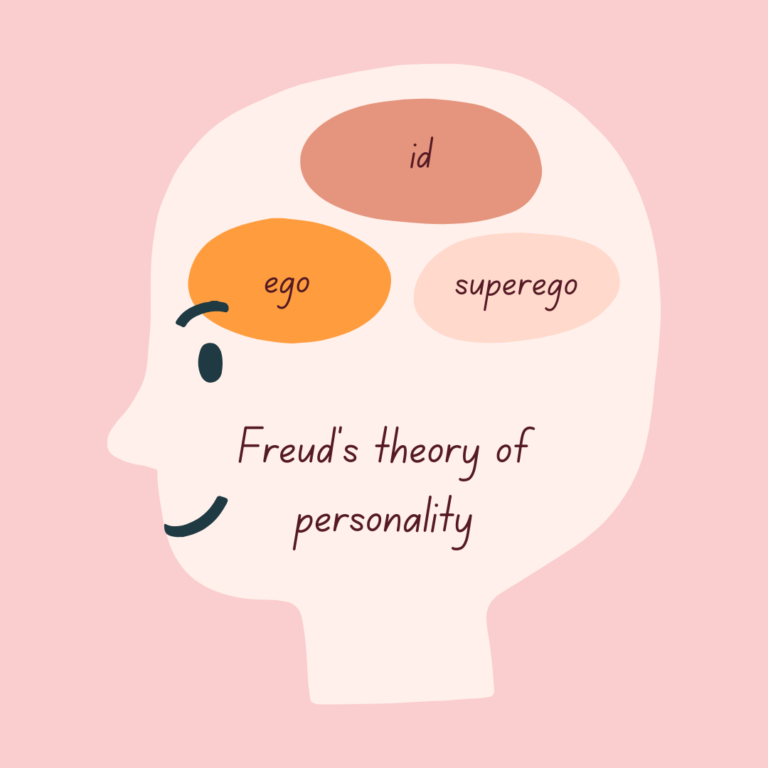
The id, ego, and superego are important are components of personality in Freud’s psychoanalytic theory. Learn more.

Practice effects, the improvements seen with repeated testing or tasks, offer insights into learning and memory—but they also raise questions about validity in research.