Bias Blind Spot: Definition and Examples
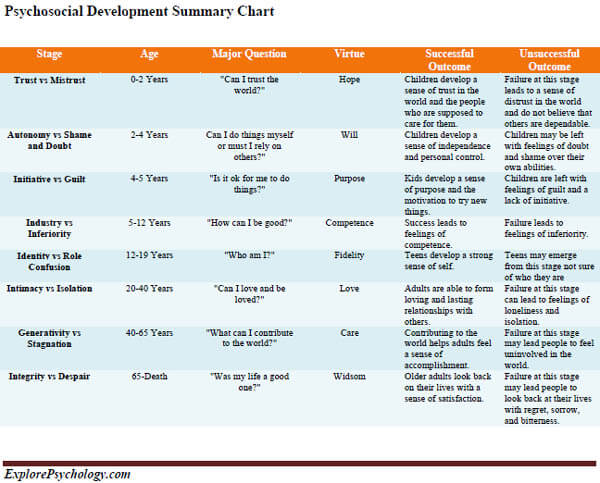
The bias blind spot is a cognitive bias that involves not being able to recognize your own biases. You probably realize that there are subtle cognitive biases that influence your perceptions and decisions. Yet, if you are like most people, you also tend to notice those biases more in other people than in yourself. This…